


Eid-ul-Fitr, often simply referred to as Eid, is one of the two major Islamic holidays celebrated by Muslims around the world, the other being Eid-ul-Adha. Eid-ul-Fitr marks the end of Ramadan, the Islamic holy month of fasting. The exact date of Eid-ul-Fitr varies each year, depending on the sighting of the moon, but it generally falls on the first day of Shawwal, the tenth month of the Islamic lunar calendar, immediately following Ramadan.
The history of Eid-ul-Fitr dates back to the time of the Prophet Muhammad, who is said to have received revelations from Allah (God) that were later compiled into the Quran, the holy book of Islam. According to Islamic tradition, the month of Ramadan was established as a time of fasting and spiritual reflection to commemorate the first revelation of the Quran to Muhammad.
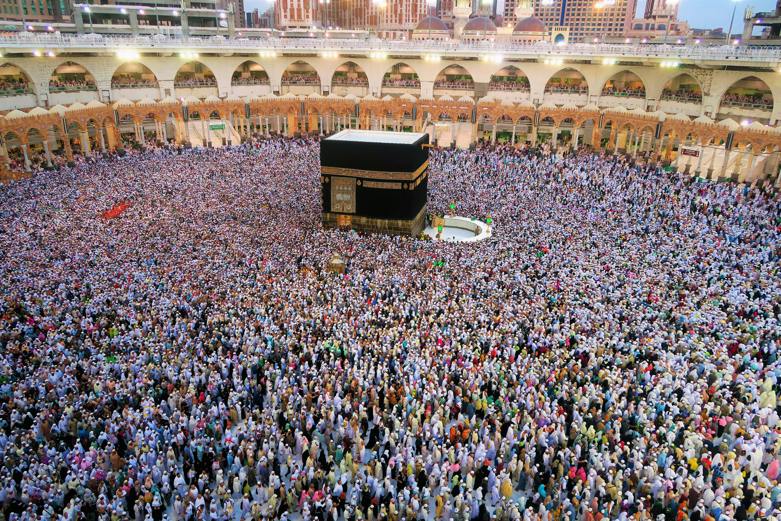
The observance of Eid-ul-Fitr typically begins with a special prayer called the Eid prayer, which is performed in congregation at mosques or open prayer grounds. The prayer is followed by a sermon, after which Muslims greet each other with the phrase "Eid Mubarak," which means "Blessed Eid" in Arabic.
Eid-ul-Fitr is a time of joy and celebration, and it is common for Muslims to wear new clothes, decorate their homes, and prepare special meals to share with family and friends. It is also a time of charity, and Muslims are encouraged to give to those in need, particularly during the month of Ramadan leading up to Eid-ul-Fitr.
Eid-ul-Fitr is special for several reasons, both religiously and culturally. Here are some key aspects that make Eid-ul-Fitr a unique and significant celebration:
End of Ramadan: Eid-ul-Fitr marks the end of Ramadan, a month of fasting, prayer, and reflection for Muslims worldwide. It is a time of spiritual growth and renewal, and Eid-ul-Fitr serves as a joyful conclusion to this period of devotion.
Celebration of Community: Eid-ul-Fitr is a time for Muslims to come together in prayer, celebration, and solidarity. It is a time to strengthen bonds with family, friends, and the larger community, fostering a sense of unity and togetherness.
Charity and Generosity: Giving to those in need is an essential part of Eid-ul-Fitr. Muslims are encouraged to perform acts of charity, known as "Zakat al-Fitr," to ensure that everyone can participate in the festivities and enjoy a special meal on Eid day.
Joyful Festivities: Eid-ul-Fitr is a joyous occasion filled with festivities and traditions. People dress in their finest clothes, decorate their homes, and prepare special meals to share with loved ones. It is a time of feasting, laughter, and happiness.
Spiritual Reflection: Eid-ul-Fitr is not just a time of celebration but also a time for spiritual reflection and gratitude. Muslims reflect on their experiences during Ramadan, seek forgiveness for any shortcomings, and express gratitude for Allah's blessings.
Cultural Traditions: Eid-ul-Fitr is celebrated with various cultural traditions and practices around the world. Each region and community may have its unique way of celebrating, including special foods, music, and customs, adding to the richness and diversity of the celebration.
Eid-ul-Fitr is celebrated with a variety of rituals and traditions that vary across different cultures and regions. However, some common rituals are observed by Muslims worldwide during this festival. Here are some key rituals of Eid-ul-Fitr:
Fasting: While not a ritual of Eid-ul-Fitr itself, fasting during Ramadan is a prerequisite for celebrating Eid-ul-Fitr. Muslims fast from dawn to sunset throughout the month of Ramadan, abstaining from food, drink, smoking, and other physical needs.
Zakat al-Fitr: Before the Eid prayer, Muslims are required to give a specific amount of money or food to the less fortunate. This charity, known as Zakat al-Fitr or Fitrana, is obligatory for every Muslim who can afford it and ensures that everyone can participate in the festivities of Eid.
Eid prayer: One of the main rituals of Eid-ul-Fitr is the Eid prayer, known as Salat al-Eid. This special prayer is performed in congregation, either at mosques or open prayer grounds, and consists of two units of prayer with additional Takbirs (saying "Allahu Akbar" or "God is Great").
Greeting: After the Eid prayer, it is customary for Muslims to exchange greetings and good wishes. The phrase "Eid Mubarak" (meaning "Blessed Eid") is commonly used to greet one another.
Family gatherings: Eid-ul-Fitr is a time for families to come together. After the Eid prayer, families often gather for a festive meal, exchange gifts, and enjoy each other's company.
Eid attire: Muslims are encouraged to wear new or their best clothes on Eid-ul-Fitr as a sign of joy and celebration.
Special foods: Different cultures have their traditional foods for Eid-ul-Fitr, but it is common to prepare sweet dishes and desserts to share with family and friends.
Visiting the graves: Some Muslims visit the graves of their loved ones during Eid-ul-Fitr to pray for their deceased relatives and friends.
Here are some unique facts about Eid-ul-Fitr that do not overlap with the common rituals:
Moon Sighting: The exact date of Eid-ul-Fitr is determined by the sighting of the new moon, which marks the end of Ramadan. This practice reflects the lunar-based nature of the Islamic calendar.
Pre-Eid Preparations: In the days leading up to Eid-ul-Fitr, Muslims often engage in thorough cleaning and decoration of their homes, preparing special foods and sweets, and shopping for new clothes and gifts.
Takbir: In the days of Eid, it is common for Muslims to recite the Takbir, which is the Arabic phrase "Allahu Akbar" (God is the Greatest), as an expression of joy and gratitude.
Eidgah: In many Muslim-majority countries, the Eid prayer is performed at a designated outdoor prayer ground called the Eidgah, rather than at mosques.
Eid Sermon: Before or after the Eid prayer, an imam delivers a special sermon, known as the Khutbah, which often focuses on gratitude, forgiveness, and unity among Muslims.
Social Responsibility: Eid-ul-Fitr emphasizes social responsibility and solidarity with the less fortunate. In addition to Zakat al-Fitr, Muslims are encouraged to engage in acts of kindness and charity throughout the Eid festivities.
Eid Traditions Around the World: While the core elements of Eid-ul-Fitr are consistent across the Muslim world, there are unique cultural traditions associated with the holiday in different regions, such as the use of henna in some countries or the practice of giving gifts to children.